Last updated
In this article, we unpack the greenhouse effect—explaining what it is, how it functions, and why it's a critical driver of global warming.
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
It is a vital natural process that warms Earth’s surface by trapping the sun’s energy in our atmosphere. Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's temperature would be around -18°C (source).
How does it work?
Solar radiations reach our atmosphere, some bounce back to space. The rest is absorbed by land, ocean and the heat re-radiated from Earth toward space. Greenhouse effect gases in our atmosphere such as carbon dioxide, methane or nitrous dioxide will trap some of the heat in our atmosphere, preventing it from reaching space. These gases act as the glass wall of the green house, thus the name of its effect.
So, what really is the problem?
Imagine a winter day in Dubai. It’s 18°C and you wear a light jacket. This jacket is the natural greenhouse effect. Now, imagine in addition of this light jacket, you wear a ski jacket. The sun is not hotter, but the heat you trap under your jackets is too much. Thus, the additional ski jacket you put on is the extra greenhouse effect due to greenhouse gases generated by human activities.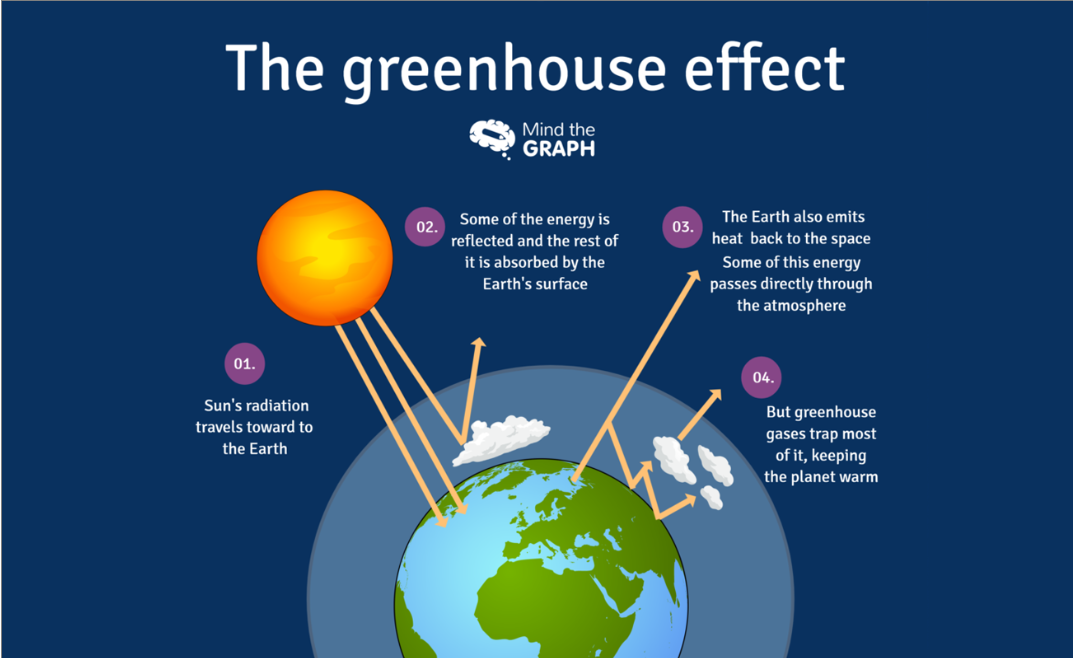
How are we sure the sun is not responsible for Global Warming?
The satellites we have in space are recording the amount of solar energy and temperature of the upper atmosphere (stratosphere): both measures confirmed Earth is receiving less solar radiation during the last 50 years. Meaning, if it’s hotter inside our atmosphere, it’s not because we receive more heat from the sun but because we trap more heat in our atmosphere.
Read more here. (source)
Read more here. (source)
More of a video person?
The Greenhouse Effect
Latest blogs

Health & Sustainability
What is the IPCC? What They Do and Why Their Reports Matter
by
:
Salma Khalifa

Lifestyle
Father’s Day 2024: 10 Best Ways to Celebrate Him
by
:
Salma Khalifa

Culture
Beginner's Guide to Choosing the Best Turntable
by
:
Salma Khalifa

Outdoors
Top 5 Places to Stargaze in the UAE
by
:
Salma Khalifa